Quelques notes glanées au fil de mes lectures sur la gestion de projets et les différentes méthodologies.
Fast-tracking #
What is fast-tracking in project management? #
Fast-tracking in project management refers to a method where tasks that would ordinarily be completed in sequential order are instead completed concurrently. Fast-tracking a project can indicate a number of things, including that the project is at risk of not finishing on time. However, it may also reflect an unrealistic deadline or even a desire to bring a product to market faster.
To use fast-tracking in project management, you must first go over the critical path and identify which tasks can be performed parallel to one another.
For example, when planning a party, you cannot hang up decorations if a venue has not first been chosen. These are two tasks that cannot run parallel to one another. However, in this same example, hanging up decorations and setting out the party snacks are two activities that can be done simultaneously to quicken the time to the end result.
What are the risks of fast-tracking in project management? #
As the PMBOK Guide points out, “fast-tracking may result in rework and increased risk.” For instance, the project may become more difficult to control because of increased complexity. The overall quality and efficiency of the work may also suffer due to tasks beginning in the middle of other tasks.
When both the fast-tracking and crashing techniques are applied, budget increase/overrun is also a possibility. This is because the crashing technique requires adding additional resources (overtime, workforce, etc.) to a project for faster completion.
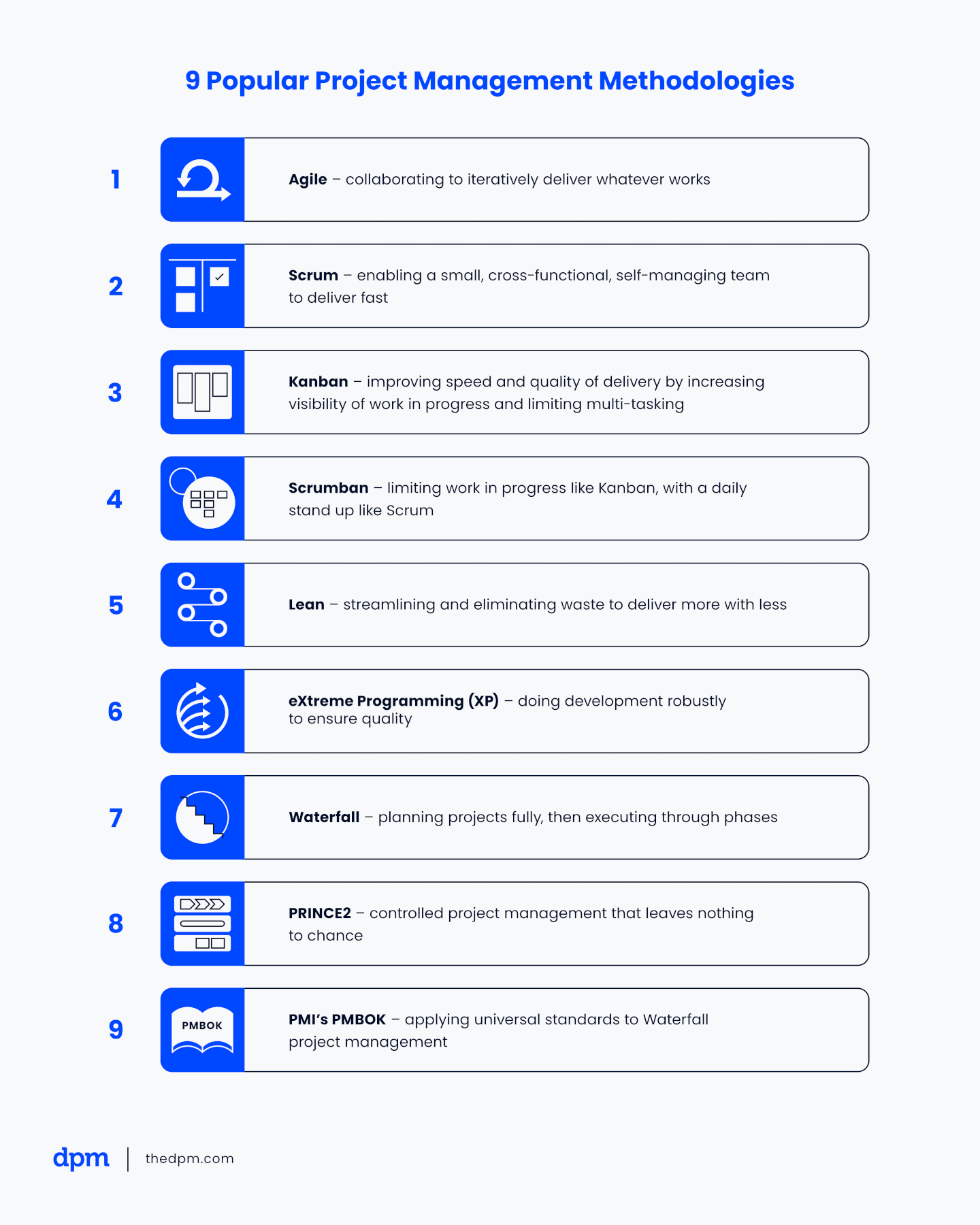
Waterfall #
There are generally two broad approaches to project management: Waterfall and Lean. Waterfall feels like an assembly line, where one thing happens after another, in sequence.
It first originated in the 1950s and is based on traditional construction and manufacturing industry processes. Waterfall doesn’t stray from the plan, aims to document and scope everything from the start.
There’s some project management purists out there who love waterfall vs lean, and vice versa of course, but generally, you can think of them as having different use cases: waterfall is great for if you have a project with a predictable outcome. You know what you’re doing and how to do it, you just need to get it done and keep everything on track.
What is the Waterfall methodology? #
The Waterfall methodology—also known as the Waterfall model—is a sequential development process that flows like a waterfall through all phases of a project (analysis, design, development, and testing, for example), with each phase completely wrapping up before the next phase begins.
It is said that the Waterfall methodology follows the adage to “measure twice, cut once.” The success of the Waterfall method depends on the amount and quality of the work done on the front end, documenting everything in advance, including the user interface, user stories, and all the features’ variations and outcomes. With the majority of the research done upfront, estimates of the time needed for each requirement are more accurate, and this can provide a more predictable release date. With a Waterfall project, if parameters change along the way, it’s harder to change course than it is with Agile methodology.
Agile #
What is Agile project management? #
Agile project management is an iterative approach to project management that focuses on breaking down large projects into more manageable tasks, which are completed in short iterations throughout the project life cycle. Teams that adopt the Agile methodology are able to complete work faster, adapt to changing project requirements, and optimize their workflow.
As the name suggests, the Agile allows teams to be better equipped to quickly change direction and focus. Software companies and marketing agencies are especially aware of the tendency for changes from project stakeholders to happen from week-to-week. The Agile methodology allows teams to re-evaluate the work they are doing and adjust in given increments to make sure that as the work and customer landscape changes, the focus also changes for the team.
Scrum #
What is Scrum? #
Scrum is a sub-category of Agile that breaks down the process more specifically. So agile is the broad umbrella focused on iteration, flexibility and collaboration, and scrum gets more specific with how that gets done.
Within scrum, there are sprints.
A sprint is a pre-defined chunk of time - often ranging anywhere from one-week to a month, but can be as short as a 1 day sprint too. At the start of a sprint, the team will hold a sprint planning meeting to prioritize the sprint’s tasks.
Another aspect of scrum is something called a standup. It can look like a short meeting where everyone mentions, very briefly, 3 things:
- what they worked on last
- what they plan on working on today/next
- blockers
Lean #
What Is Lean Project Management? #
Lean project management is the application of lean manufacturing principles to the practice of project management. The goal of lean project management is to maximize value while minimizing waste. Lean manufacturing principles were developed by Toyota in the 1950s and applied in the 1970s to combat the energy crisis. The term “lean” was coined in the late 1980s. The Project Management Institute sums it up: “To be Lean is to provide what is needed, when it is needed, with the minimum amount of materials, equipment, labor, and space.”
Lean manufacturing identifies three types of waste: muda, muri, and mura (known collectively as the 3M).
Muda refers to activities that consume resources without providing additional value
Muri refers to the overuse of equipment or employees
Mura is operational “unevenness,” which decreases efficiency and productivity in the long term
Lean project management aims to reduce the 3M within the project process.
Timeboxing #
In Agile principles, timeboxing allocates a fixed and maximum unit of time to an activity, called a timeboxing, within which planned activity takes place. It is used by Agile principles-based project management approaches and for personal time management.